Echinococcosis (Hydatid Cyst)
Key Facts
Terminology
Synonyms
Hydatidosis, echinococcosis
Definition
Infectious condition caused by tapeworms
Etiology/Pathogenesis
4 types of Echinococcus
E. granulosus
E. multilocularis
E. vogeli
E. oligarthrus
Clinical Issues
Epidemiology
Worldwide distribution
Predominantly in sheep- and cattle-raising regions
Symptoms
Cough
Dyspnea
Hemoptysis
Pneumothorax
Infection can also involve
Liver
Brain
Spleen
Kidney
Bone
Natural history
Eggs can contaminate fruits, vegetables, water, or hands
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Hydatidosis, echinococcosis
Definitions
Infectious condition caused by tapeworms
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infectious Agents
Echinococcus
4 types
E. granulosus
E. multilocularis
E. vogeli
E. oligarthrus
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Worldwide distribution
Predominantly in sheep- and cattle-raising regions
Age
Can occur in any age group
Gender
Appears to be more common in females
Ethnicity
No ethnic predilection
Presentation
Symptoms
Cough
Chest pain
Dyspnea
Hemoptysis
Pneumothorax
Infection can involve
Lung
Liver
Brain
Spleen
Kidney
Bone
Patients may be asymptomatic
Natural History
Eggs can contaminate fruits, vegetables, water, or hands
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete surgical resection of the cyst
Drugs
Albendazole
Combined mebendazole with praziquantel
Prognosis
Good after treatment
Can develop serious morbidity
IMAGE FINDINGS
General Features
Cystic lesion
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
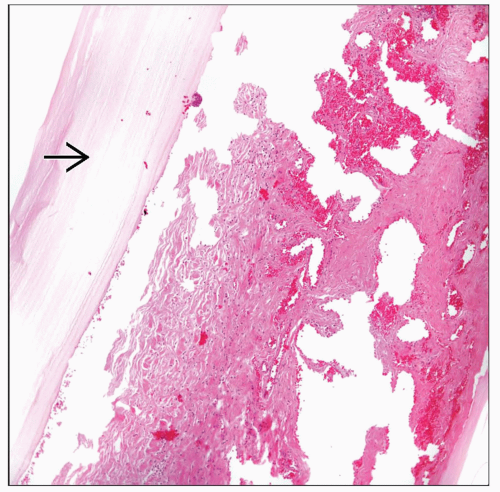
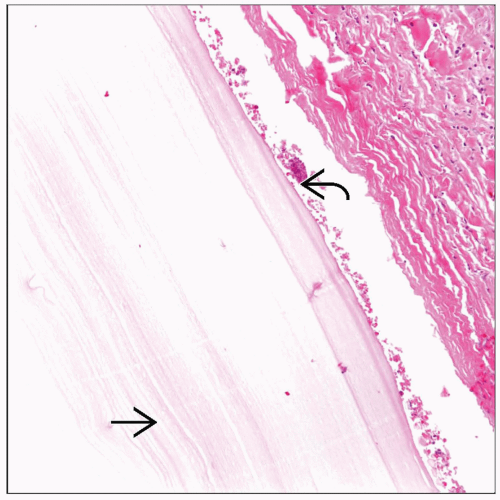
Unilocular or multilocular cysts
Thin walls
Light tan fluid contents
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Bronchopneumonia
Abscess formation
Identification of the parasite
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree