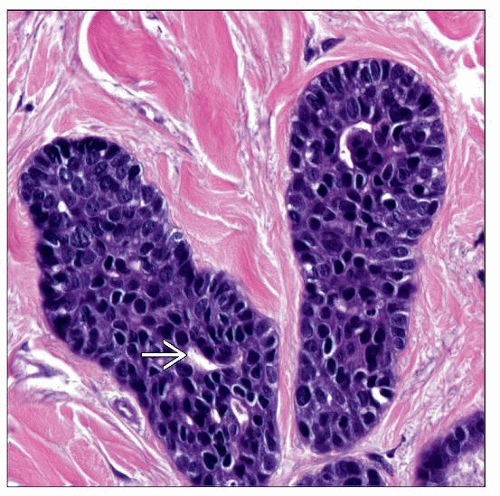
Eccrine Carcinoma
Steven D. Billings, MD
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Typically present as plaque on scalp
Locally aggressive
Microscopic Pathology
Infiltrative growth pattern, often with perineural invasion
Tumor composed of basaloid epithelium with uniform hyperchromatic nuclei
Tumor forms epithelial strands with lumen formation
May have “hand mirror” shape similar to syringoma
Lumina highlighted by EMA &/or CEA
Top Differential Diagnoses
Microcystic adnexal carcinoma
Presence of keratocysts allows for distinction (absent in eccrine carcinoma)
Adenoid cystic carcinoma
Cribriform architecture allows distinction (generally absent in eccrine carcinoma)
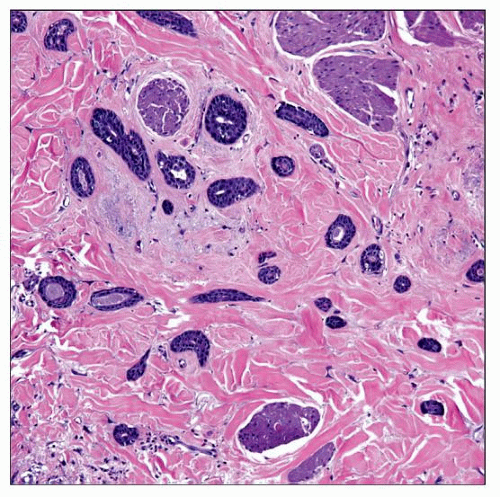 Eccrine carcinoma is characterized by an infiltrative growth pattern. The tumor forms glandular and duct-like structures that lack the organized appearance of normal eccrine glands. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Syringoid carcinoma, syringoid eccrine carcinoma, eccrine syringomatous carcinoma, eccrine epithelioma
Definitions
Malignant adnexal tumor with eccrine differentiation somewhat resembling a syringoma
No evidence of association with or development from syringomas
Some authorities group these tumors with microcystic adnexal carcinoma (MAC)
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Very rare tumors
Age
Usually present in middle-aged patients
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree