Drug-related Steatohepatitis/Phospholipidosis
Laura Webb Lamps, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Definition: Steatohepatitis as consequence of drug exposure
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Commonly implicated drugs
Amiodarone
Methotrexate
Antiretroviral drugs
Nifedipine
Clinical Issues
Symptoms may present after months to years of therapy
May be asymptomatic despite liver injury
Especially methotrexate injury
Due to long half-life of amiodarone, may take months to see improvement
Risk of liver damage with methotrexate use depends on duration of therapy and dose
Exacerbated by concomitant obesity, alcohol use
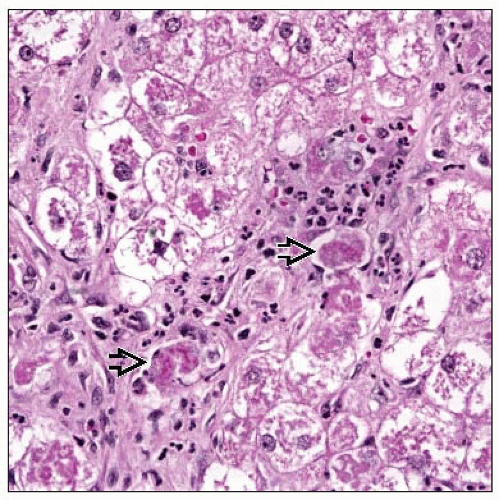
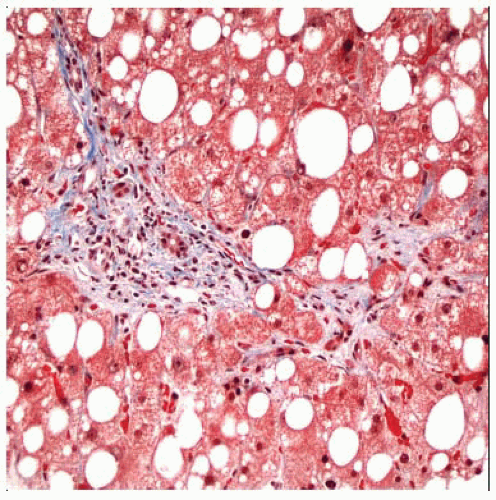
Microscopic Pathology
Amiodarone
Steatosis
Phospholipidosis
Mallory hyaline, often with associated neutrophils (satellitosis)
Methotrexate
Steatosis
Reactive changes
Fibrosis
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Steatohepatitis as consequence of drug exposure
Some seem to produce their effect by exacerbating underlying nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Commonly Implicated Drugs
Amiodarone (antiarrhythmic)
Strongly tissue-bound, becomes concentrated in liver
Nifedipine (calcium channel blocker)
Perhexiline maleate (calcium channel blocker)
Methotrexate (immunosuppressant/antineoplastic)
Hepatic injury usually occurs after long-term use
Tamoxifen (estrogen antagonist)
Steroids
Naproxen (NSAID)
Trimethoprim-Sulfa (antibiotic)
Total parenteral nutrition
Steatosis particularly seen in adults
Anti-HIV drugs
Induce syndrome of dyslipidemia, fat maldistribution, insulin resistance
Known as HIV-associated lipodystrophy syndrome or HIV-associated metabolic and morphological abnormality syndrome (HAMMAS)
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Variably present constitutional complaints, hepatomegaly, jaundice
May be asymptomatic (especially methotrexate injury)
Symptoms may present after months to years of therapy
Laboratory Tests
Elevated transaminases
May be normal despite hepatic injury, especially in patients on methotrexate
Prognosis
Amiodarone
Cessation of therapy should lead to regression of injury
Due to long half-life of drug, may take months to see improvement
If drug is not withdrawn, process can progress to cirrhosis, hepatic failure
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree