Digital Fibromatosis (Infantile Digital Fibromatosis)
Elizabeth A. Montgomery, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Benign proliferation of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts containing scattered eosinophilic inclusion bodies that occur on digits of young children
Clinical Issues
Rare fibroblastic/myofibroblastic neoplasm
Occurs usually in 1st year of life
Dorsal aspects of hands or feet
Presents with digital enlargement
Dome-shaped swelling overlying phalanges or interphalangeal joints
Extradigital soft tissues (i.e., arm, breast) are extremely rarely affected
May recur locally, but excellent prognosis
May show spontaneous regression
Local excision with preservation of function
Macroscopic Features
Ill-defined neoplasms
Microscopic Pathology
Infiltrating fascicles
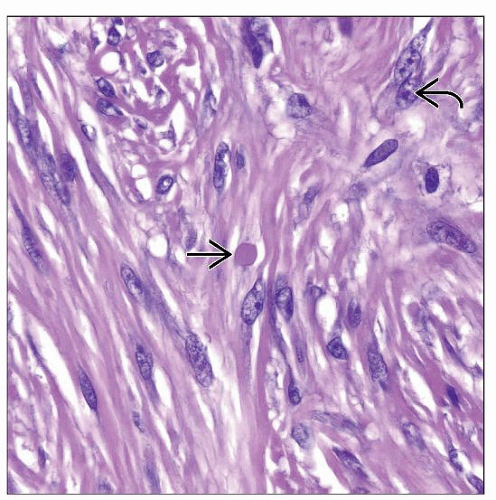
Uniform spindle-shaped tumor cells
No significant cytologic atypia
Pale eosinophilic, fibrillary cytoplasm
Intracytoplasmic eosinophilic spherical inclusions
Inclusions are trichrome positive
Ancillary Tests
Spindled cells show features of myofibroblasts
Expression of actins, desmin, calponin, and CD99
Inclusions show granular &/or filamentous features by EM
Cytoplasmic filaments extend onto inclusions
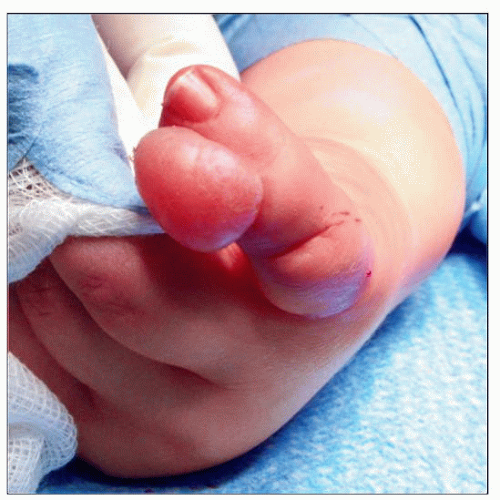 Clinical examination of infantile digital fibromatosis shows an exophytic, dome-shaped superficial neoplasm, which presents in infants and small children. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Infantile digital fibromatosis
Digital fibrous tumor of childhood
Inclusion body fibromatosis
Definitions
Benign proliferation of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts, containing scattered eosinophilic spherical inclusions, that arises on the digits of young children
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare fibroblastic/myofibroblastic neoplasm
Age
Most cases occur in 1st year of life
Very rare in adult patients
Gender
M = F
Site
Dorsal aspects of hands or feet most common
Rarely synchronous or asynchronous involvement of more than 1 digit
Thumb or great toe is only very rarely affected
Extradigital soft tissues (i.e., arm, breast) are only extremely rarely affected
Presentation
Digital enlargement
Dome-shaped swelling overlying phalanges or interphalangeal joints
Nontender nodules
Rarely erosion of bone
Natural History
May recur locally
May regress spontaneously
No progression
No metastases
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Local excision with preservation of function
Prognosis
Excellent overall prognosis
May recur locally
May show spontaneous regression
Main prognostic indicator is adequacy of primary excision
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Ill-defined neoplasm
Dermal-based neoplasm with gray-white, indurated cut surface covered by intact skin
No areas of hemorrhage
No areas of necrosis
Size
Nodules of variable size
Usually measure < 2 cm
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Infiltrating fascicles and sheets
Uniform-appearing spindle-shaped fibroblasts and myofibroblasts
No significant cytologic atypia
Elongated spindled nuclei
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree