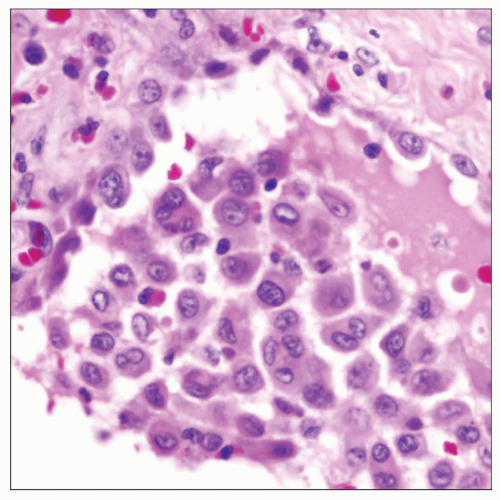
Desquamative Interstitial Pneumonia
Key Facts
Terminology
A distinctive histologic reaction pattern to lung injury related to cigarette smoking
Clinical Issues
Dyspnea
Cough
Cessation of smoking generally leads to regression of symptoms and radiologic changes
Patients with moderate to severe disease respond well to administration of corticosteroids
Much better survival than UIP and other interstitial pneumonias
Image Findings
Bilateral symmetric areas of ground-glass opacification in lower lung zones
Reticular pattern observed in 50% of cases due to localized areas of fibrosis
Microscopic Pathology
Histologic hallmark is diffuse and extensive intraalveolar deposition of alveolar macrophages
Minimal fibrosis with only mild thickening of alveolar septa and mild chronic inflammatory infiltrate
Absence of organizing fibroblastic foci
All lesions in same stage of evolution (absence of “temporal heterogeneity”)
Ancillary Tests
Cells filling alveoli are positive for CD68 macrophage-associated antigen and negative for cytokeratin
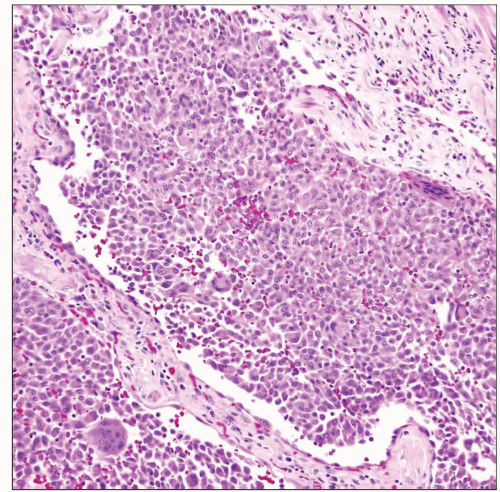 Desquamative interstitial pneumonia shows plugging and distention of airspaces by monotonous infiltrate of alveolar macrophages filling the lumen. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP)
Definitions
A distinctive histologic reaction pattern to lung injury related to cigarette smoking
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Strong epidemiologic link to cigarette smoking
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Unknown
Age
40-50 years
Gender
More common in males (2:1)
Presentation
Dyspnea
Cough
Crackles on auscultation
Clubbing in 40% of patients
Laboratory Tests
Lung function tests show a restrictive pattern with decreased diffusion capacity
Natural History
Subacute onset (weeks to months) of symptoms
Cessation of smoking generally leads to regression of symptoms and radiologic changes
Patients with moderate to severe disease respond well to administration of corticosteroids
Recurrences occur when patients resume smoking
Treatment
Steroids
Smoking cessation
Prognosis
Much better survival than UIP and other interstitial pneumonias
Approximately 95% 5-year survival and 70% 10-year survival
Very small number of patients may progress to diffuse interstitial fibrosis requiring transplantation
IMAGE FINDINGS
Radiographic Findings
Bilateral symmetric areas of ground-glass opacification in lower lung zones
Reticular pattern observed in 50% of cases due to localized areas of fibrosis
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree