Desmoplastic Small Round Cell Tumor
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Most common in children and young adults (median age: 20 years)
Male predilection
Large pleural-based mass on chest x-rays and CT scans
Poor prognosis
Median survival is 24 months
Macroscopic Features
Large, bulky tumors (> 10 cm in greatest dimension)
Microscopic Pathology
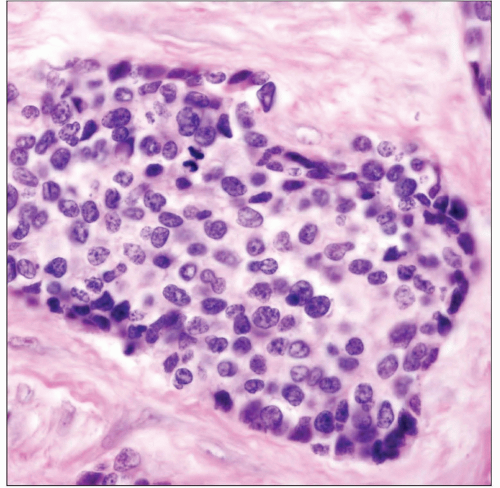
Nests, trabeculae, or sheets of small round blue cells embedded in abundant desmoplastic fibrous stroma
Rosette-like structures
Small to intermediate-sized round to oval cells with scant cytoplasm
High mitotic rate, often with atypical (abnormal) mitoses
Staining pattern is polyphenotypic
Vimentin, keratin, desmin, EMA, and WT1 consistently stain tumor cells in ˜ 90% of cases
Staining pattern for desmin and vimentin is characteristically dot-like and paranuclear
May also show focal positivity for CD56, NSE, chromogranin, synaptophysin, and S100 protein
Shows t(11:22)(p13;q12), similar to Ewing sarcoma/PNET
Unlike Ewing sarcoma, site on chromosome 11 is WT-1 gene rather than FLI-1 gene
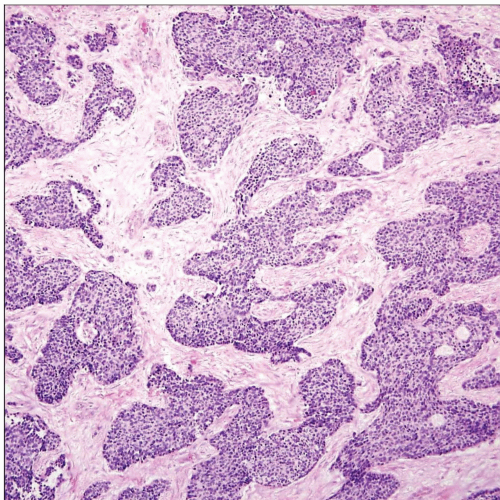 Desmoplastic small round cell tumor of the pleura shows islands of small round blue tumor cells surrounded by abundant, paucicellular, and desmoplastic connective tissue stroma. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Desmoplastic small round cell tumor (DSRCT)
Synonyms
Desmoplastic small cell tumor with divergent differentiation
Polyphenotypic small round cell tumor
Desmoplastic primitive neuroectodermal tumor
Definitions
Primitive malignant neoplasm arising in serosal surfaces with distinctive histology composed of primitive small round blue cells embedded in abundant desmoplastic stroma
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Unknown
May represent primitive mesothelial neoplasm (i.e., “mesoblastoma”)
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Male predilection
Pain and weight loss
Large pleural-based mass on chest x-rays and CT scans
Most common in children and young adults (median age: 20 years)
Treatment
Surgical excision
Chemotherapy
Prognosis
Poor prognosis
Frequent local recurrence; rarely metastasizes
Median survival is 24 months
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Large, bulky tumors (> 10 cm in greatest dimension)
May also grow in multinodular fashion
Firm, homogeneous cut surface
Hemorrhage and necrosis
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Nests, trabeculae, or sheets of small round blue cells embedded in abundant desmoplastic fibrous stroma
Nests may display peripheral palisading of tumor cells
Rosette-like structures
Cytologic Features
Small to intermediate-sized round to oval cells with scant cytoplasm
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree