Dermatophytosis
Christine J. Ko, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Superficial fungal infection secondary to dermatophytes
Dermatophytes belong to 3 genera
Trichophyton, Epidermophyton, Microsporum
Clinical Issues
Classic lesion
Annular plaque of erythema with scale at advancing border
Microscopic Pathology
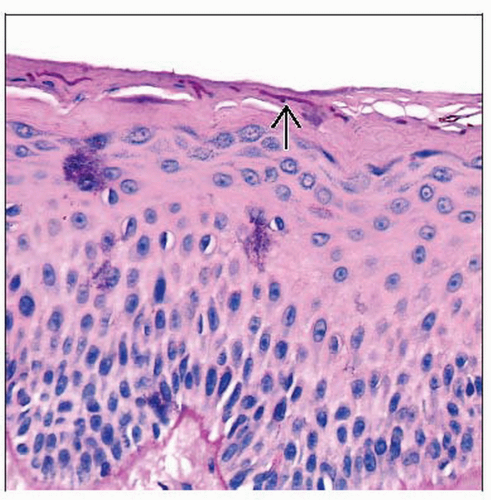
Skin infection
Clue: Neutrophils in stratum corneum
Clue: “Sandwich” sign: Parakeratosis or compact orthokeratosis underlying basket-woven stratum corneum (dermatophytes located in between)
Fungal stain(s) highlight hyphae
Majocchi granuloma
Fungal hyphae tracking down into hair follicles
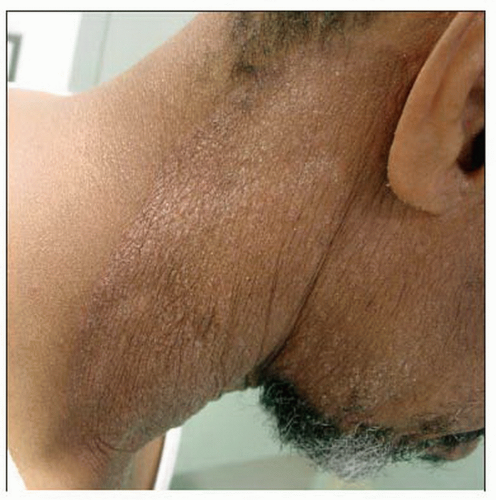 There is an erythematous, scaly plaque with lichenification on the neck and jawline of this patient. KOH examination of the scale showed fungal hyphae. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Ringworm, tinea, tinea capitis, tinea faciei, tinea barbae, tinea corporis, tinea cruris, tinea manuum, tinea pedis, tinea unguium, onychomycosis, tinea gladiatorum, tinea imbricata
Definitions
Superficial fungal infection secondary to dermatophytes
Dermatophytes belong to 3 genera
Trichophyton
Epidermophyton
Microsporum
Dermatophytes preferentially infect humans (anthropophilic), animals (zoophilic), or soil (geophilic)
Common anthropophilic dermatophytes
Trichophyton rubrum
Trichophyton violaceum
Common zoophilic dermatophytes
Microsporum canis
Trichophyton verrucosum
Common geophilic dermatophytes
Microsporum gypseum
Dermatophytes can infect skin (generally located in stratum corneum), hair (with exception of Epidermophyton), &/or nails
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree