Chronic (Ductopenic) Rejection
Matthew M. Yeh, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Microscopic Pathology
Atypical bile duct epithelium resembling dysplasia
Centrizonal perivenular hepatocyte dropout
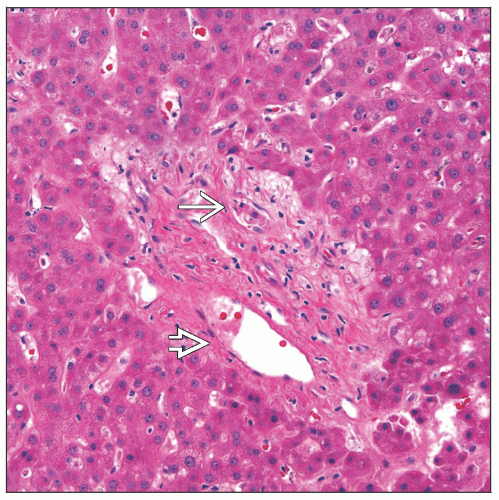
Loss of interlobular bile ducts
> 50% of portal tracts do not have interlobular bile ducts in 20 portal tracts examined
PAS stain with diastase digestion or CK7 or CK19 immunohistochemical stains may help identify bile ducts
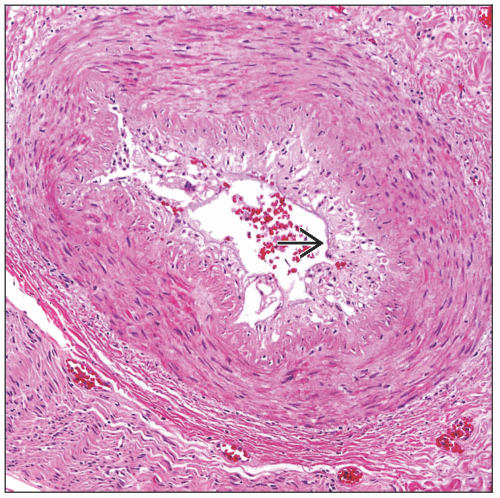
Foam cell arteriopathy
Luminal narrowing by subintimal foam cells
Top Differential Diagnoses
Ischemic cholangiopathy
Recurrent primary biliary cirrhosis
Recurrent primary sclerosing cholangitis
Vanishing bile duct syndrome in drug-induced liver disease
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Chronic rejection (CR)
Synonyms
Ductopenic rejection
Definitions
Presents in 2 forms
Obliterative (foam cell) arteriopathy
Only seen in large- and medium-sized arteries
Bile duct loss
Most common finding in allograft biopsy
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree