Chronic Cholecystitis
Kari D. Caradine, MD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Almost always associated with gallstones
Clinical Issues
More common in women; approximately 3:1
Microscopic Pathology
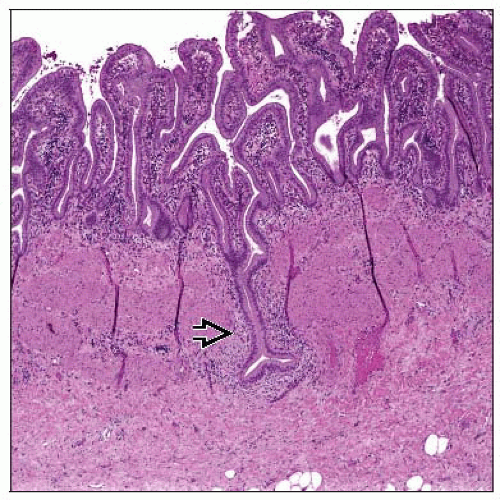
Predominantly mononuclear inflammatory infiltrate with lymphocytes dominating over plasma cells and histiocytes
Minor component of eosinophils and neutrophils may be present
Wall thickening secondary to muscular hypertrophy and fibrosis
Metaplastic changes; most common is antral type
Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses
Diagnostic Checklist
Presence of gallstones is neither necessary nor sufficient for diagnosis of chronic cholecystitis
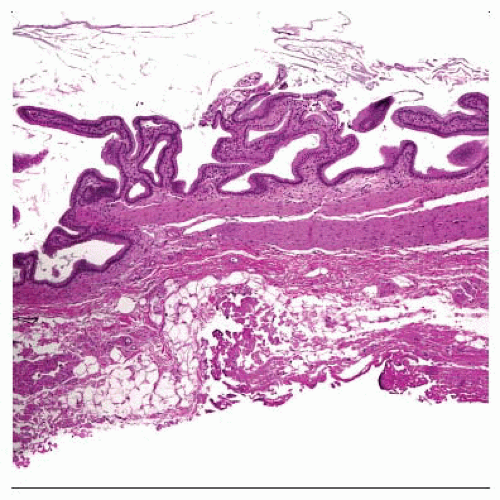 This section illustrates a normal gallbladder with typical wall thickness and a normal complement of chronic inflammatory cells. |
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Chronic inflammation of gallbladder
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Pathogenesis
Poorly understood
Almost always associated with gallstones
Possible association with trauma induced by gallstones, prior episodes of acute cholecystitis, or abnormal composition of bile
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Age
Patients in their 40s or 50s
Gender
More common in women (3:1)