Cholelithiasis
Kari D. Caradine, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Stones in gallbladder or common bile duct
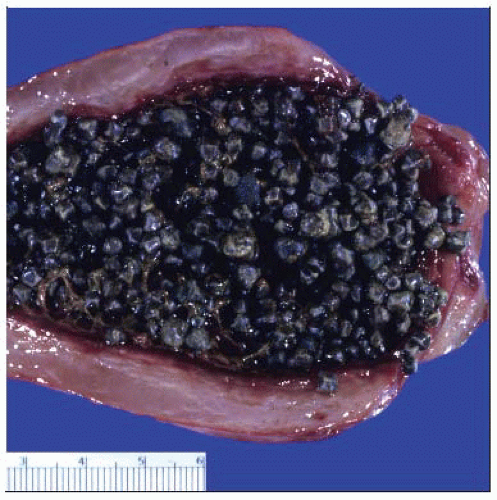
Classified by chemical composition into 2 main types: Cholesterol stones and pigment stones
Clinical Issues
Majority of stones are cholesterol stones (> 80%)
Most gallstones are clinically silent
Symptoms usually consist of right upper quadrant pain, flatulence, and intolerance of fatty food
Macroscopic Features
Cholesterol stones contain > 75% cholesterol with smaller amounts of calcium bilirubinate
Pigment stones consist predominantly of calcium bilirubinate, with smaller amounts (< 25%) of cholesterol
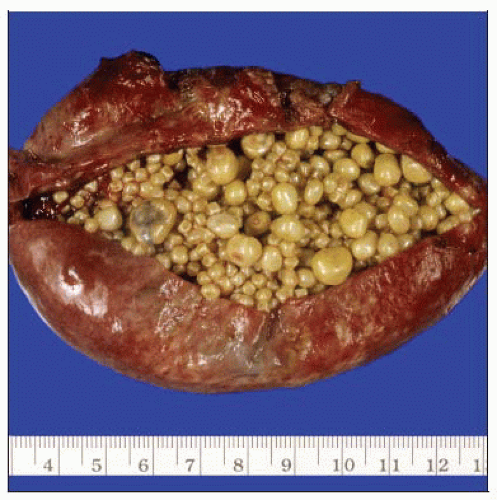 Gross photograph shows a gallbladder filled with numerous smooth yellow cholesterol stones. The gallbladder wall is mildly thickened and hyperemic. (Courtesy G. F. Gray, MD.) |
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Stones in gallbladder or common bile duct
Classified by chemical composition into 2 main types: Cholesterol stones and pigment stones
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Cholesterol Stone Formation
Bile, supersaturated with cholesterol, is secreted by liver
Nucleation or initiation of stone formation
Growth to detectable size
Pigment Stone Formation
Increase in bile concentration of unconjugated bilirubin, which combines with calcium
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Variable in different parts of world
In United States, estimated 10-20% of population have gallstones
Majority of stones are cholesterol stones (> 80%)
Associated with obesity, multiparity, rapid weight loss, estrogen replacement therapy, oral contraceptive use, hypertriglyceridemia, Crohn disease, and total parenteral nutrition (TPN)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree