Castleman Disease
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Most common in 3rd decade of life
Localized type
Presents as large mass involving lymph node or lymph node group
Many patients are asymptomatic, and mass is discovered incidentally on chest x-rays
Multicentric type
Most often encountered in setting of HIV and HHV8 infection
Multicentric cases are symptomatic and require combination chemotherapy and steroids
Microscopic Pathology
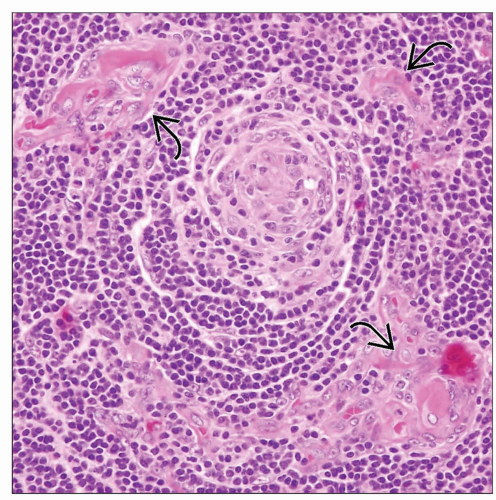
Hyaline-vascular type is most common type encountered in mediastinum
Characterized by follicular abnormalities and interfollicular hypervascularity
Enlarged follicles with thickened mantle zones and almost complete obliteration of germinal centers
Enlarged follicles containing 2 or more germinal centers
Concentric layering of mantle zone lymphocytes around follicles (“onion skin” appearance)
Increased number of vessels in interfollicular spaces admixed with lymphocytes, plasma cells, plasmacytoid monocytes, and immunoblasts
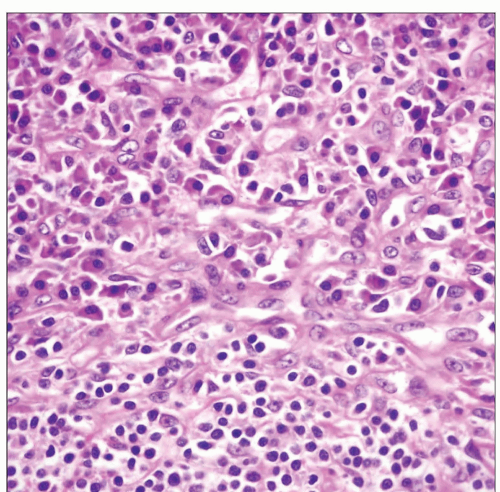
Plasma cell type is most common type seen in multicentric disease but may also be localized
Most characteristic feature is distention of interfollicular spaces by sheets of polyclonal plasma cells
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Giant lymph node hyperplasia, angiofollicular lymph node hyperplasia, angiomatous lymphoid hamartoma
Definitions
Heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by lymph nodal enlargement and lymphoid hyperplasia with stromal changes
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Pathogenesis
Unknown etiology and pathogenesis
Some cases of plasma cell variant may be related to infection with HHV8 (Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpes virus)
Some cases are associated with autoimmune diseases such as Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome and AIDS
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Affects males and females equally
Most common in 3rd decade of life
May also affect children and elderly patients
Site
Most common location is anterior mediastinum
May also involve middle and posterior mediastinum
Presentation
Localized type
Broad age range
Most common histologic features are those of hyaline-vascular type
Presents as large mass involving lymph node or lymph node group
Compression of airways leads to shortness of breath
Compression of vascular structures can lead to esophageal varices
Most patients are asymptomatic, and mass is discovered incidentally on routine x-rays
Multicentric type
Most often found in setting of HIV and HHV8 infection
Most cases histologically correspond to plasma cell variant
B symptoms (fever, night sweats) occur in 95% of patients
Hepatosplenomegaly, body cavity effusions, skin rash can also be seen
Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, LDH, IL-6, thrombocytopenia, and polyclonal hypergammaglobulinemia are common
Treatment
Localized cases are cured with simple surgical excision
Multicentric cases require combination chemotherapy and steroid treatment
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Hyaline-vascular type
Most common type encountered in mediastinum
Characterized by follicular abnormalities and interfollicular hypervascularity
Enlarged follicles with thickened mantle zones and almost complete obliteration of germinal centers
Enlarged follicles containing 2 or more germinal centers
Small, burned-out follicles with atrophy of germinal centers
Focal hyalinization of atrophic follicles simulating Hassall corpuscles
Concentric layering of mantle zone lymphocytes around follicles (“onion skin” appearance)
Replacement of follicles by pale, epithelioid cells admixed with small vessels with hyalinized walls
Tangentially cut vessels seen penetrating germinal center (“lollipop sign”)
Increased number of vessels in interfollicular spaces admixed with lymphocytes, plasma cells, plasmacytoid monocytes, and immunoblasts
Hyalinization of interfollicular areas with dense bands of sclerosis
Prominence of follicular dendritic cells in follicles
Cases with dysplastic dendritic follicular cells may develop into follicular dendritic cell sarcomas
“Stroma-rich” variant is characterized by massive replacement of interfollicular areas by sclerotic vessels and spindle cells
Plasma cell type
Most common type seen in multicentric disease but may also be localized
Closely associated with HIV and HHV8 infections
Most characteristic feature is distention of interfollicular spaces by sheets of polyclonal plasma cells
Follicles may be normal or show some features seen in hyaline-vascular variant
Large, atypical plasmablastic cells are present in mantle zones in HHV8(+) cases
Kaposi sarcoma and malignant lymphomas can develop from or coexist in lymph nodes with plasma cell type
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree