Calcified Fibrous Pseudotumor
Key Facts
Terminology
Calcified fibrous pseudotumor (CFPT)
Clinical Issues
Cough
Chest pain
Shortness of breath
Asymptomatic
Macroscopic Features
Single pleural mass
Multiple pleural nodules
Microscopic Pathology
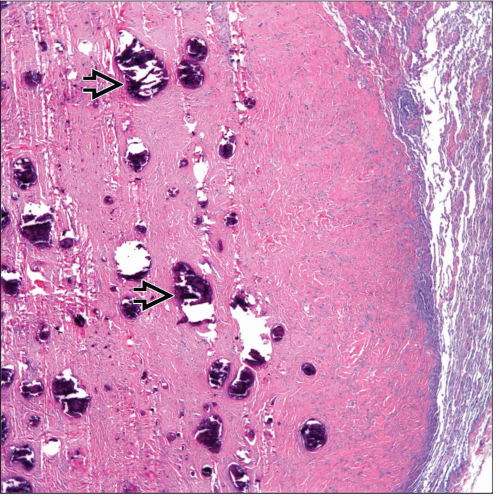
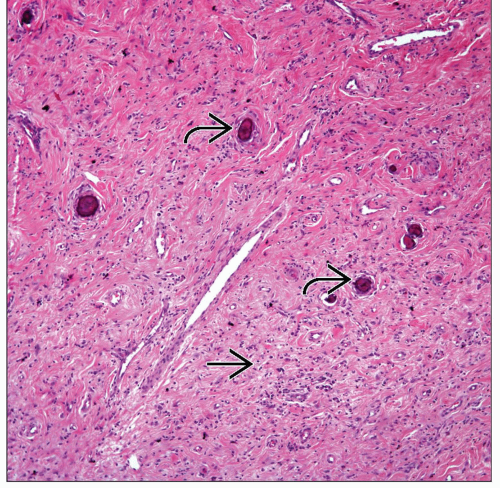
Dense fibrocollagenous tissue
Psammoma bodies
Dystrophic calcifications
Lymphoplasmacytic inflammatory reaction
Absence of nuclear atypia or mitotic activity
Absence of necrosis &/or hemorrhage
Top Differential Diagnoses
Solitary fibrous tumor
Shows different growth pattern in same tumor
Positive staining for Bcl-2
Rarely shows dystrophic calcification &/or psammoma bodies
Sarcomatoid mesothelioma
Shows diffuse pleural involvement
Shows nuclear atypia and mitotic activity
Positive for CK-PAN
Fibrous plaque
CFPT generally shows psammoma bodies &/or dystrophic calcification
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Calcified fibrous pseudotumor (CFPT)
Definitions
Benign fibrocollagenous tumor with dystrophic or psammomatous calcifications
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Possible Etiologies
Fibroinflammatory in nature
Reactive process
Late sclerosing stage of myofibroblastic tumor
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Very uncommon tumor in thoracic cavity
Age
Usually occurs in adults from 20-55 years old
Gender
No gender predilection
Presentation
Cough
Chest pain
Shortness of breath
Asymptomatic
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete surgical resection
Prognosis
Good
Recurrences may occur
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Single pleural mass
Multiple pleural nodules
Size
Tumors may vary from 1 cm to > 10 cm in diameter
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Dense fibrocollagenous tissue
Psammoma bodies
Dystrophic calcifications
Lymphoplasmacytic inflammatory reaction
Absence of nuclear atypia or mitotic activity
Absence of necrosis &/or hemorrhage
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Fibrous
Predominant Cell/Compartment Type
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree