Biliary Cystadenoma and Cystadenocarcinoma
Matthew M. Yeh, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Biliary cystadenoma almost exclusively occurs in women
CA19-9 and CEA in cyst fluid helps differentiate between simple cyst and biliary cystic neoplasm
Macroscopic Features
Solitary, multiloculated cystic neoplasm
Clear, mucinous, or opalescent cystic fluid
Cyst lining may be smooth, trabeculated, or have papillary excrescences
Thickened, nodular areas suggest malignancy
Microscopic Pathology
Similar to mucinous cystic neoplasm of pancreas
Cystadenoma
Lined by mucinous columnar epithelium with focal cuboidal, flattened, or papillary areas
May have gastric or intestinal metaplasia
Varying degrees of dysplasia may be present
Densely cellular ovarian-like stroma positive for estrogen and progesterone receptors and inhibin
Cystadenocarcinoma
Most arise from preexisting cystadenoma
Invasion of underlying stroma by malignant glands or single cells
Top Differential Diagnoses
Cystic variant of biliary intraductal papillary neoplasm
Solitary bile duct cysts
Ciliated hepatic foregut cyst
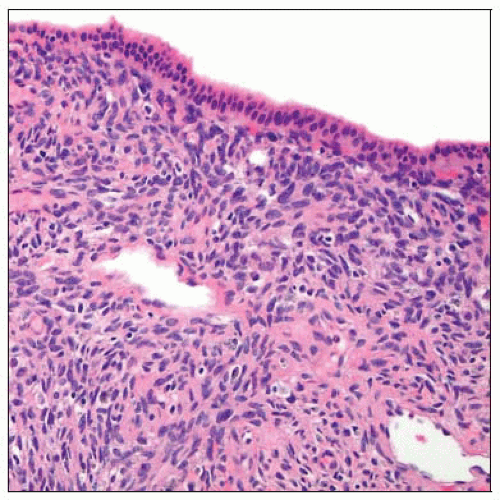 The classic spindled and cellular ovarian-type stroma is seen underneath the cyst lining of a biliary cystadenoma. |
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Cystic biliary neoplasm arising within liver
May arise in extrahepatic biliary tree, including gallbladder
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Unknown
May arise from gallbladder precursor elements or peribiliary glands
Most cystadenocarcinomas arise from preexisting biliary cystadenoma
Some may represent cystic variant of cholangiocarcinoma
Occasionally may arise in biliary cysts
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare; < 5% of cystic lesions of liver
Age
Average is 40-50 years
Gender
Biliary cystadenoma almost exclusively occurs in women
Biliary cystadenocarcinoma may be seen in men, given varied pathogenesis
Presentation
Pain, mass, and occasionally jaundice
Some patients are asymptomatic
Laboratory Tests
CA19-9 and CEA in cyst fluid helps differentiate between simple cyst and biliary cystic neoplasm
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete resection
Prognosis
Surgical resection should be curative
Incompletely resected tumor may recur or undergo malignant transformation
IMAGE FINDINGS
Ultrasonographic Findings
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree



