|
Typical Clinical Features |
Microscopic Features |
Ancillary Investigations |
Neuroma, traumatic |
Painful nodule on or near nerve, following trauma |
Nonencapsulated, multiple nerve bundles of varying size randomly dispersed in fibrous tissue |
S100 protein+ (Schwann cells), EMA+ (perineurial cells), NF+ (axons) |
Neuroma, mucosal |
Oral cavity, eyelids, gastrointestinal tract
Associated with MEN type IIb |
Nonencapsulated aggregate of uniformly sized nerve bundles |
S100 protein+ (Schwann cells), EMA+ (perineurial cells), NF+ (axons) |
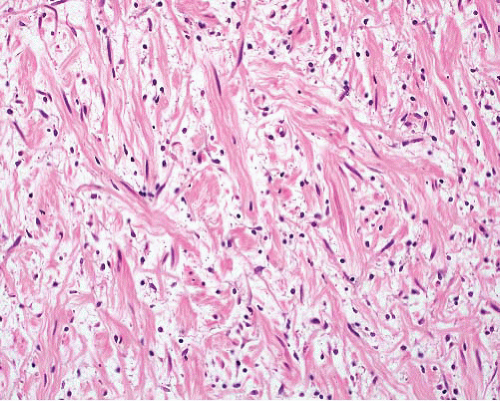
Neurofibroma, regular |
Any location, associated NF1
Nonencapsulated |
Mixture of wavy spindle cells, collagen fibers (“shredded-carrot”), mast cells |
S100 protein+ (not all cells), EMA+ very rarely focally, CD34+ focally
NF+ in axons |
Neurofibroma, diffuse |
Some associated with NF1
Children and young adults
Head and neck, subcutaneous infiltrative plaque
Associated with plexiform neurofibroma—extends outside nerve bundles into soft tissue |
Sheets of short spindle cells in loose fibrous stroma, infiltrating between normal structures
Wagner-Meissner bodies in various stages |
S100 protein+ diffusely in nuclei |
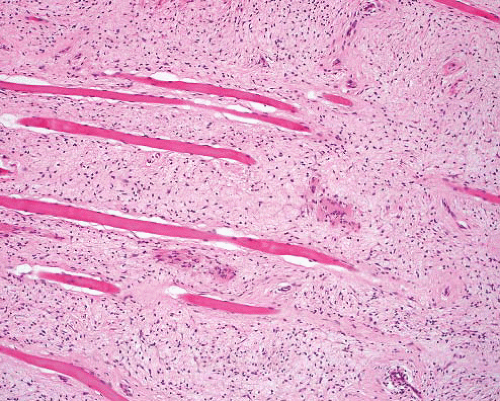
Neurofibroma, plexiform |
Associated with NF1
Can involve large nerves in deep locations or more superficial ones
Can undergo malignant change
Can extend extraneurally as diffuse neurofibroma |
Transitions from normal nerve
Nerve expanded by variable myxoid stroma and increased cellularity
Atypical variant has nuclear crowding, pleomorphism
Diffuse extraneural component in some |
S100 protein+ focally, EMA+ in peripheral perineurial cells
NF+ in axons |
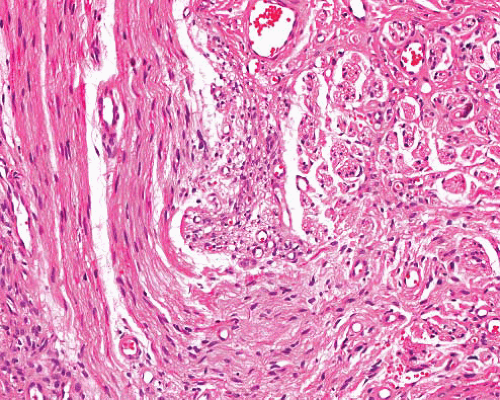
Perineurioma |
Skin, subcutis, most locations
Subset in colon
Intraneural, sclerosing, reticular and plexiform variants |
Spindle cells with long thin nuclei and very long slender terminal processes, in fascicles or perivascular whorls
Fibrous or myxoid stroma |
EMA+, claudin-1+, GLUT-1+, CD34+ in some, beta-catenin− |
Angiofibroma of soft tissue |
Superficial or deep, lower extremity, near joints, female predominance |
Circumscribed, bland spindle cells, prominent thin-walled vessels and ectatic spaces |
EMA+, CD34±, SMA±, desmin±
t(5;8)(p15;q13),
AHRR–NCOA2 fusion |
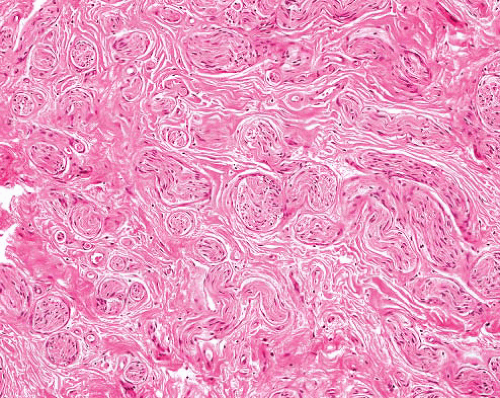
Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma |
Skin, deep soft tissue, limbs/girdles |
Fibromatosis-like areas, swirling fibromyxoid transitions, cellular myxoid areas without pleomorphism
Some nuclei are lozenge shaped, no nucleoli
Giant collagenous rosettes |
MUC4+, EMA+, occasionally SMA+, claudin-1+ in some
Nuclear beta-catenin usually negative
t(7;16)(q33;p11) FUSCREB3L2 or t(11;16) (p13;p11) FUS-CREB3L1 fusion, rarely
t(11;22)(p13;q12) EWSR1-CREB3L1 fusion |
Fibromatosis— desmoid type |
Deep in limbs, head and neck, body cavities |
Parallel myofibroblasts evenly dispersed in collagen, slit-like and thick-walled small-caliber vessels, perivascular and interstitial mast cells |
SMA+, nuclear betacatenin+, CD34− |
Fibromatosis— superficial |
Palm, sole, penis; infiltrative plaque |
Variably cellular nodules in dense collagen
Cells are parallel aligned, lack atypia
Mast cells |
SMA+, nuclear betacatenin + occasionally, CD34− |
Palisaded encapsulated neuroma |
Small nodule on face, adults |
Thinly encapsulated, Schwann cells associated with axons, perineurial cell “capsule”
Similar to schwannoma but more axons |
S100 protein+ (Schwann cells), EMA+ (perineurial cells), NF+ (axons) |
Schwannoma |
Any location, nerve of origin
Encapsulated (except in gastrointestinal tract, nose, bone)
Cellular, plexiform, myxoid, epithelioid, and melanotic variants |
Antoni A areas with palisading and Verocay bodies, Antoni B areas with spindle cells in myxoid stroma
Cyst formation, thick-walled vessels, thrombi, hemosiderin |
S100 protein+ diffusely, EMA+ in peripheral perineurial cells, CD34+, GFAP+, CK+ occasionally |
Schwannoma, cellular |
F > M, middle age
Paravertebral in retroperitoneum or pelvis can erode bone
Also submucosal in nose, stomach, or intestine (no capsule) |
Thick capsule, subcapsular lymphoid aggregates
Fascicles of cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm, focal pleomorphism, occasional mitoses
Lacks Antoni A and B areas
Lymphocytes, clusters of foamy cells, thick-walled vessels, hemosiderin |
S100 protein+ diffusely CD34+ focally, GFAP+ focally, podoplanin+ focally, occasional CK+ |
Ganglioneuroma |
Retroperitoneum, mediastinum |
Neurofibromatous background with ganglion cells of variable maturity |
S100 protein+ in spindle cells, NSE+, CD56+, NF+ in ganglion cells |
Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor |
M > F
In NF1 or sporadic, axial, or in limbs
Origin in nerve or neurofibroma |
Variably cellular and myxoid, fascicular pattern
Nuclei wavy, buckled or lanceolate, with one blunt end
Palisading, neuroid whorls, vascular wall involvement, rare small collagenous “rosettes”
Heterologous elements—rhabdomyosarcoma, osteosarcoma, angiosarcoma, epithelial glands |
S100 protein+ (65%), occasional GFAP+, CK+ (but not usually CK7 or CK19) |
MEN, multiple endocrine neoplasia; NF, neurofibromatosis; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein. |