Aspergillosis
Andrew C. Walls, BSc
Chad Jessup, MD, MS
Martin C. Mihm, Jr., MD
Key Facts
Terminology
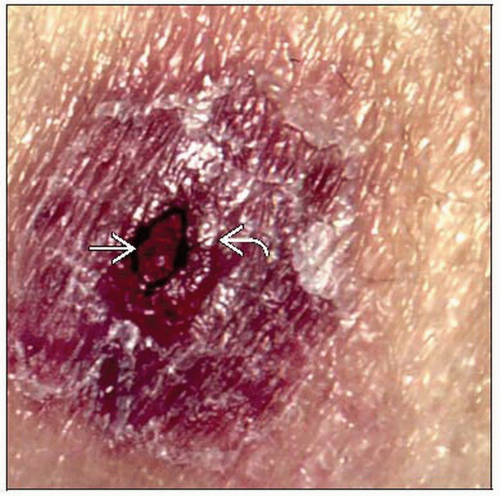
Cutaneous fungal infection due to angioinvasive Aspergillus spp.
Clinical Issues
Key risk factor: Immunocompromise
Primary cutaneous lesions arise from direct local inoculation/colonization
Secondary cutaneous lesions arise from hematogenous dissemination usually of sinobronchopulmonary origin
Microscopic Pathology
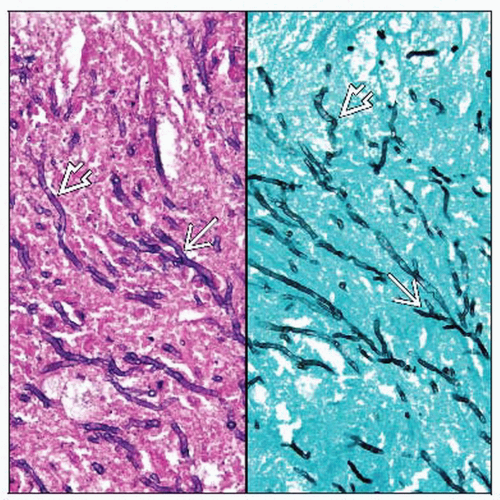
2-4 µm septated hyaline hyphae with dichotomous branching at 45° angle
Angioinvasion, overlying tissue ischemic necrosis and hemorrhage
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Cutaneous fungal infection due to angioinvasive Aspergillus spp.
Primary cutaneous lesions arise from direct local inoculation/colonization
Host is most often immunocompromised or, rarely immunocmpetent
Secondary cutaneous lesions arise from hematogenous dissemination, usually of sinobronchopulmonary origin, in immunocompromised host
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Ubiquitous soil and water-dwelling fungal organism
Contact made through direct inhalation of spores (conidia) or primary inoculation of skin
Hospital renovations or construction may increase ambient spore count
Infectious Agents
A. fumigatus, A. flavus most common (70%)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree