Angiosarcoma
Laura Webb Lamps, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Most common primary hepatic sarcoma
Etiology/Pathogenesis
25-40% of cases associated with vinyl chloride, Thorotrast, arsenic, or steroids
Clinical Issues
Predominantly older patients, strong male predominance
Liver biopsy may result in bleeding and death
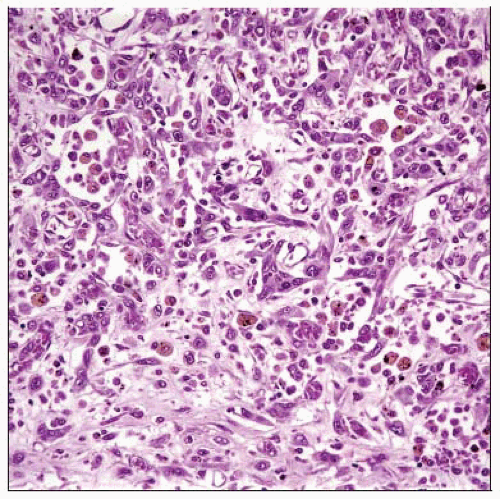
Microscopic Pathology
Proliferation of malignant endothelial cells in vascular structures
Eventually destroys hepatic parenchyma
Solid, epithelioid, and spindled areas may be present
Immunopositive for vascular markers
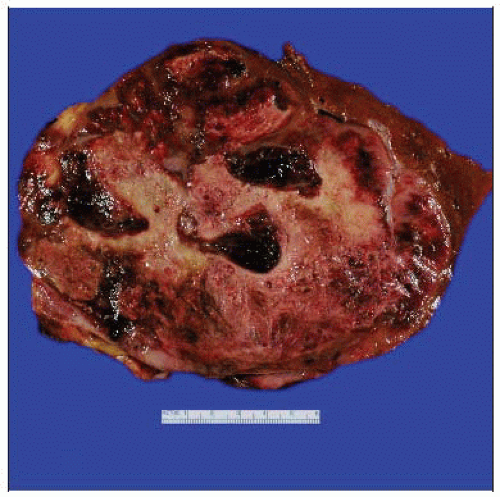 This cross section from a partial hepatectomy for angiosarcoma shows numerous cystic, blood-filled spaces. (Courtesy C. Trower, PA (ASCP) and A. Folpe, MD.) |
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Rare malignant vascular tumor of liver
Most common primary hepatic sarcoma
Approximately 2% of malignant liver tumors
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Drugs/toxins
Vinyl chloride
Arsenic
Thorotrast
Androgens
Contraceptive steroids
Copper sulfate
Diethylstilbestrol
Phenelzine
About 25-40% of cases associated with vinyl chloride, Thorotrast, arsenic, or steroids
Many of these agents no longer used or strictly controlled, but they have very long latency period of up to several decades after exposure
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology