Angiosarcoma
Key Facts
Macroscopic Features
Diffuse, plaque-like growth encasing pleura
Abundant hemorrhage and necrosis
Infiltration of adjacent structures
Microscopic Pathology
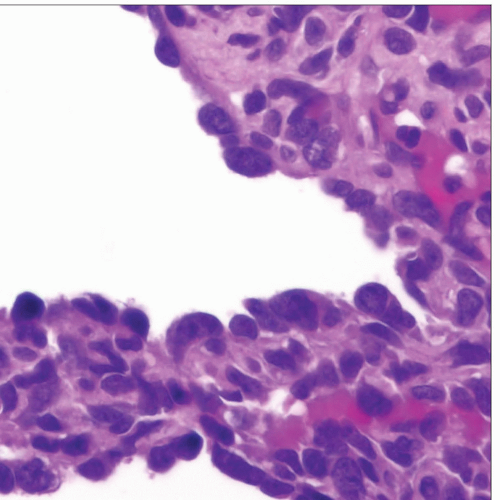
Solid atypical epithelioid or spindle cell proliferation
Anastomosing vessel-like channels lined by atypical cells
Extensive hemorrhage and necrosis
Enlarged nuclei with dense chromatin pattern
Prominent nucleoli
Frequent mitoses, including atypical (abnormal) mitoses
Cells may be predominantly epithelioid (epithelioid variant of angiosarcoma) and resemble an epithelial neoplasm
Conventional type is composed of spindle and pleomorphic tumor cells resembling spindle cell sarcoma
CD31 and CD34 positive in tumor cells
Cytokeratin may be positive in cells of epithelioid variant
Tumor cells are negative for most conventional mesothelioma markers
Diagnostic Checklist
May simulate malignant mesothelioma radiologically and histologically
Characterized by recurrent hemorrhagic pleural effusion
Prognosis is similar to that of malignant mesothelioma
Not associated with asbestos exposure
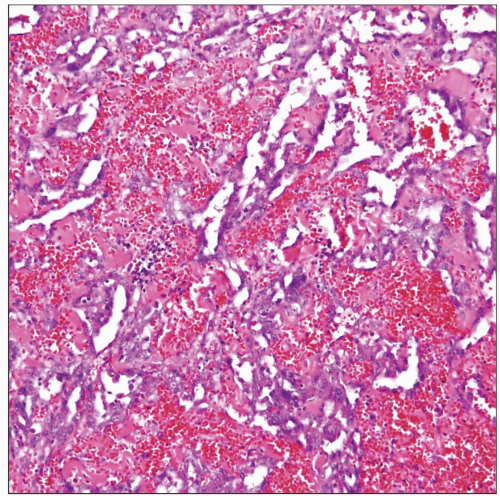 The pleura in pleural angiosarcoma is replaced by an extensively hemorrhagic cellular proliferation composed of anastomosing vessel-like channels that are lined by large, atypical endothelial cells. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Angiosarcoma (AS)
Definitions
Malignant pleural neoplasm showing evidence of vascular endothelial differentiation
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Unknown
No association with occupational exposure to asbestos
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Chest pain
Dyspnea
Recurrent hemorrhagic pleural effusions
Age range: 22-79 years (average: 57 years)
History of prior chronic pyothorax reported in Japan
Treatment
Surgical excision
Radiation therapy
Chemotherapy
Prognosis
Poor prognosis
Highly aggressive behavior
Median survival approximately 12 months
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Diffuse, plaque-like thickening encasing pleura
Abundant hemorrhage and necrosis
Infiltration of adjacent structures
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Solid atypical epithelioid or spindle cell proliferation
Anastomosing vessel-like channels lined by atypical cells
Extensive hemorrhage and necrosis
Infiltration of adjacent structures
Cytologic Features
Enlarged nuclei with dense chromatin pattern
Prominent nucleoli
Frequent mitoses, including atypical (abnormal) mitoses
Cells may be predominantly epithelioid (epithelioid variant of angiosarcoma) and resemble an epithelial neoplasm
Conventional type is composed of spindle and pleomorphic tumor cells resembling a spindle cell sarcoma
ANCILLARY TESTS
Immunohistochemistry
CD31, CD34, and FVIIIRAg positive in tumor cells
Cytokeratin may be (+) in cells of epithelioid variant
Tumor cells are negative for most conventional mesothelioma markers
Tumors cells are strongly positive for vimentin
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Epithelioid Malignant Mesothelioma
Typical tubulo-papillary growth pattern of epithelioid mesothelioma is absent in angiosarcoma
Angiosarcoma tends to be more hemorrhagic than mesothelioma
Presence of vessel-like spaces lined by atypical cells is rare in mesothelioma and typical of angiosarcoma
CD31 and CD34 are negative in mesothelioma
Tumor cells of epithelioid angiosarcoma may be positive for cytokeratin, similar to mesothelioma
Tumor cells in mesothelioma are positive for calretinin, CK5/6, WT1, HBME-1, and other mesothelioma markers
Metastatic Adenocarcinoma
Solid growth pattern and epithelioid cell features in angiosarcoma may simulate metastasis of carcinoma
Epithelioid angiosarcoma may be positive for cytokeratin
Anastomosing vessel-like channels favor angiosarcoma
Tumor cells will be positive for a variety of epithelial markers in metastatic carcinoma, such as EMA/MUC1, CEA-M, MOC31, TTF-1, etc.
Tumor cells will be positive for CD31 and CD34 in angiosarcoma
Clinical history or evidence of carcinoma elsewhere favors a metastatic carcinoma
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree