Anemia of Chronic Disease
Qian-Yun Zhang, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
Form of anemia seen in acute or chronic inflammatory conditions, infections, end-stage organ failure, or malignancies
Clinical Issues
Anemia itself is mild and nonprogressive
Microscopic Pathology
Normochromic, normocytic
Low reticulocyte count
Normal number of erythroid progenitors
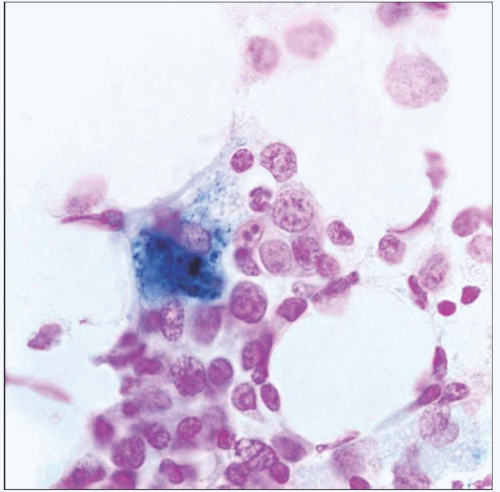
Increased storage iron in macrophages and histiocytes
Decreased number of sideroblasts (iron-containing erythroid progenitors)
Top Differential Diagnoses
Iron deficiency anemia
Anemia with chronic renal failure
Multifactorial anemia
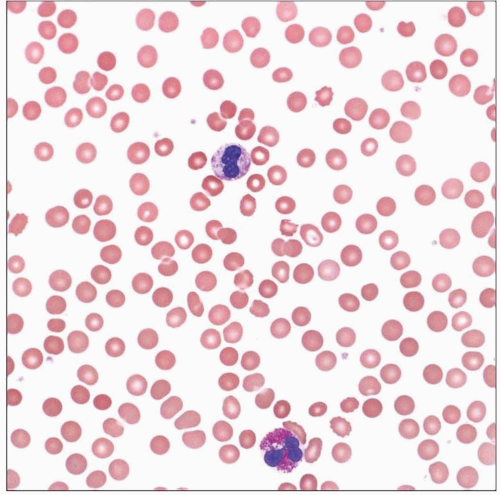 Peripheral blood smear at high power from a patient with anemia of chronic disease shows mild anisocytosis of the erythrocytes. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Anemia of chronic disease (ACD)
Synonyms
Anemia of inflammation
Definitions
Form of anemia seen in acute or chronic inflammatory conditions, infections, end-stage organ failure, or malignancies
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Iron Metabolic Disturbances
Cytokines/other immune regulatory factors (e.g., hepcidin) cause multiple iron metabolic disturbances
Decreased iron absorption in gastrointestinal (GI) tract
Accumulation of iron in reticuloendothelial system
Inability to release stored iron to plasma; hypoferremia
Diminished iron available to erythroid progenitors for hemoglobin synthesis
Suppressed erythropoiesis
Blunted bone marrow response to erythropoietin
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Mild anemia
Symptoms related to underlying disease, which usually predominates
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree