Ampulla/Bile Duct/Pancreatic Duct Adenocarcinoma
Blythe K. Gorman, MD
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Primary sclerosing cholangitis and stents may cause marked reactive atypia
Cytopathology
Nuclear molding, chromatin clumping, ↑ N:C ratio, nuclear pleomorphism, irregular nuclear membranes, prominent nucleoli, and loss of cell cohesion are important features of malignancy
Necrotic background and single intact atypical cells are worrisome for malignancy
High-grade dysplasia and invasive carcinoma may be morphologically indistinguishable
Ancillary Tests
UroVysion assay uses FISH to assess for numerical abnormalities of chromosomes 3, 7, 17, and 9p21
Polysomy is the abnormality most strongly linked to malignancy
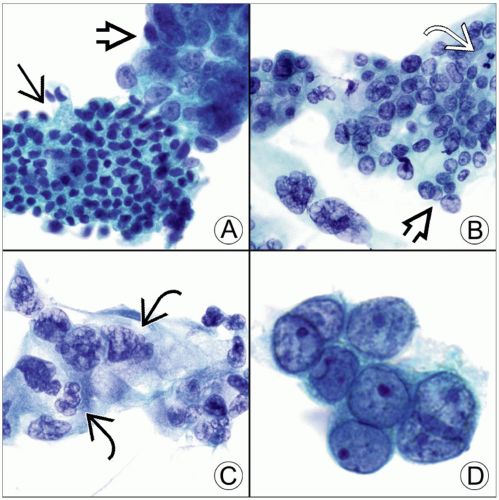 Each panel shows a Pap-stained bile duct brushing with adenocarcinoma. (A) Benign ductal cells
 arranged in an orderly sheet are dwarfed by the disorganized cluster of malignant cells arranged in an orderly sheet are dwarfed by the disorganized cluster of malignant cells 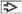 . (B) Loose cluster of malignant cells shows nuclear crowding, overlap . (B) Loose cluster of malignant cells shows nuclear crowding, overlap 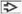 , and pleomorphism. A mitotic figure , and pleomorphism. A mitotic figure 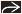 is also present. (C) Malignant cells are arranged in a syncytial group and have vesicular chromatin and irregular nuclear contours is also present. (C) Malignant cells are arranged in a syncytial group and have vesicular chromatin and irregular nuclear contours  . (D) Tumor cells have prominent nucleoli, nuclear crowding, and a high N:C ratio with very scant cytoplasm. . (D) Tumor cells have prominent nucleoli, nuclear crowding, and a high N:C ratio with very scant cytoplasm.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|