Acute Cholecystitis
Vikram Deshpande, MD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Acute calculous cholecystitis: 95% of cases
Acute acalculous cholecystitis: 5% of cases
Clinical Issues
Right upper quadrant pain, tenderness, and guarding
Fever, leukocytosis
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is procedure of choice
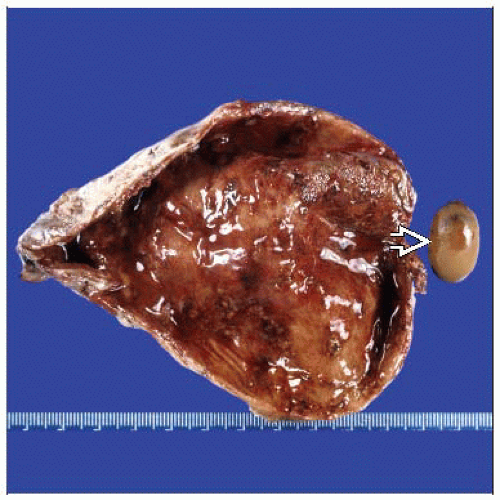
Macroscopic Features
Mural thickening, congestion, purulent exudate, adhesions
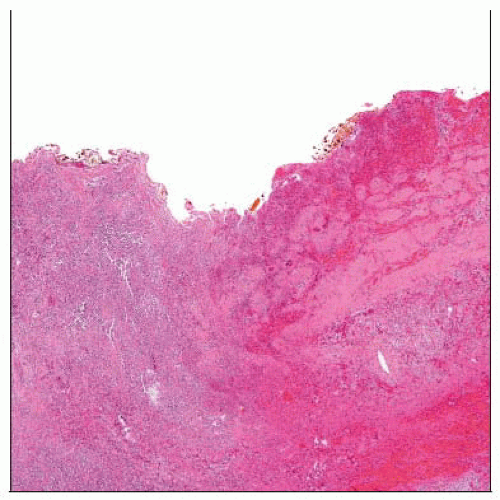
Microscopic Pathology
Changes depend on duration of disease
Inflammation may be sparse in early disease
Congestion, edema, variable necrosis
Widespread fibroblastic proliferation
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Acute inflammation of gallbladder
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Acute Calculous Cholecystitis
Key elements are obstruction of cystic duct by stones and bile supersaturated with cholesterol
Trauma to mucosa releases phospholipase from lysosomes
Phospholipase converts lecithin in bile to lysolecithin, which damages gallbladder epithelium
Secondary bacterial infection with enteric organisms occurs in 20% of cases
Overgrowth by gas-producing organisms leads to emphysematous cholecystitis
Acute Acalculous Cholecystitis
Accounts for 5% of cases
Risk factors
Critical illness, burns, trauma, major surgical procedures, diabetes, immunosuppression
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree