Acquired Erythrocytosis
Kathryn Foucar, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Hgb/Hct/RBC count above age-/sex-related normal ranges
Erythrocytoses are further subclassified into primary, secondary, and relative erythrocytosis
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Primary erythrocytosis
May be constitutional/familial due to inherited mutations in erythropoietin (EPO) receptor
May be acquired, clonal hematopoietic stem cell disorder (polycythemia vera)
Secondary erythrocytosis
EPO-mediated
Physiologically appropriate or inappropriate excess EPO production
Relative erythrocytosis due to reduced plasma volume
Clinical Issues
Plethora in patients of all ages
Severe hyperviscosity symptoms cause lethargy and cyanosis in neonates
Gaisbock syndrome
Triad of smoking, hypertension, and obesity
CBC with differential: Elevated hemoglobin, hematocrit, RBC count
Reticulocyte count
Inappropriately elevated in cases of primary and secondary erythrocytosis
Normal in relative erythrocytosis
Serum EPO level
Reduced in primary acquired erythrocytosis
Increased in all types of secondary erythrocytosis
Normal in relative erythrocytosis
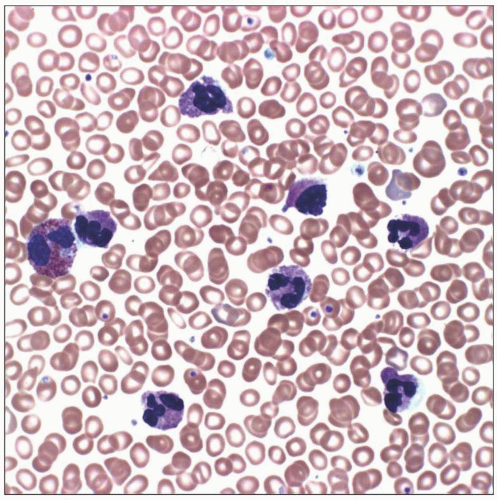
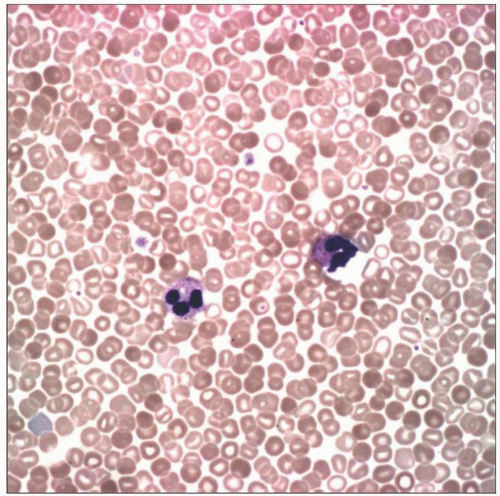 Peripheral blood smear from a patient with severe chronic hypoxia shows secondary erythrocytosis requiring ongoing phlebotomy. Note closely packed microcytic, hypochromic red blood cells. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Polycythemia
Definitions
Hgb/Hct/RBC count above age-/sex-related normal ranges
Erythrocytoses are further subclassified into primary, secondary, and relative erythrocytosis
Primary and secondary erythrocytosis show true increase
Relative erythrocytosis
Hemoconcentration secondary to reduced plasma volume
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Multifactorial Causes
Primary erythrocytosis
Erythropoietin (EPO)-independent overproduction of RBCs
May be constitutional/familial due to inherited mutations in EPO receptor (familial primary erythrocytosis)
May be acquired, clonal hematopoietic stem cell disorder (polycythemia vera)
Secondary erythrocytosis
EPO-mediated
May be constitutional/familial due to mutations in oxygen sensing apparatus
May be acquired disorder with excess EPO production
Overproduction of EPO may be physiologically appropriate or inappropriate
Acquired physiologically appropriate erythrocytosis includes residence at high altitude and other chronic hypoxic conditions
Acquired physiologically inappropriate erythrocytoses
Multiple renal disorders
EPO-producing tumors (uterine leiomyoma, renal cell carcinoma, cerebellar hemangioblastoma, parathyroid carcinoma)
Drug-associated causes
Androgen therapy or illicit use
Human recombinant EPO use
Relative erythrocytosis
Hemoconcentration results from dehydration &/or excess fluid loss
Major causes include renal and GI disorders
Gaisbock syndrome
Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome with massive pulmonary capillary leak
Pathogenesis
Erythropoietin synthesis
Oxygen sensing pathway modulates EPO gene expression
Produced in kidney in response to decreased oxygen supply to tissues
Regulated by hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)
Constitutional/familial disorders due to inherited mutations in oxygen sensing genes in rare kindreds (Chuvash region)
Acquired primary erythrocytosis (polycythemia vera)
JAK2 point mutation results in constitutive activation of nonreceptor tyrosine kinase
Dysregulated cell proliferation
Excess RBC production is independent of EPO binding to EPO receptor on progenitor cells
Acquired secondary erythrocytosis
Excess RBC production is linked to excess EPO production
Physiologically appropriate in chronic hypoxia
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree