Necrotizing Otitis Externa
Bruce M. Wenig, MD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
External otitis related to Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection
Clinical Issues
Diabetic, chronically debilitated, or immunologically deficient patients
Primarily affects older patients
Mortality rates may exceed 75% if diagnosis and treatment are delayed
Microscopic Pathology
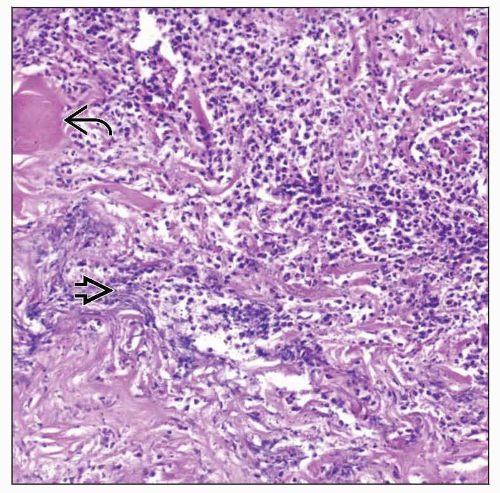
Histology dominated by presence of necrotic material and exuberant granulation tissue
Diffuse heavy acute and chronic inflammation present in subcutis extending to bone
Necrotizing vasculitis commonly present
Thick, acellular collagen seen replacing most of subcutis
Necrotic bone and cartilage
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Necrotizing external otitis (NEO)
External auditory canal (EAC)
Synonyms
“Malignant” external otitis
Necrotizing granulomatous otitis
Definitions
Virulent and potentially fatal form of external otitis related to Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree