Fibromatosis
Elizabeth A. Montgomery, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Palmar fibromatosis: Dupuytren contracture, Dupuytren disease
Plantar fibromatosis: Ledderhose disease
Penile fibromatosis: Peyronie disease
Deep fibromatosis: Aggressive fibromatosis, desmoid tumor
Myofibroblastic proliferations with infiltrative growth pattern that are prone to local recurrences but do not metastasize
Clinical Issues
Palmar fibromatosis
4-6% of Caucasian adults over 50 years of age
Deep fibromatosis
2.4-4.43 new cases per 100,000 persons per year (Scandinavian data)
Recurrences common for both superficial and deep fibromatoses
Occasional deaths from deep fibromatoses, especially FAP-associated mesenteric fibromatosis
Microscopic Pathology
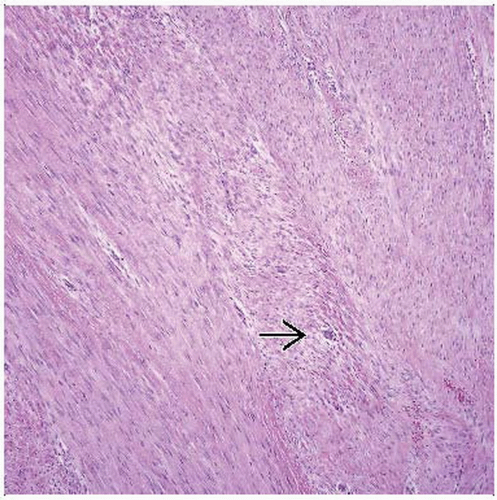
Sweeping fascicles of myofibroblasts
Smooth nuclear membranes
Delicate nucleoli in most cells
Occasional cells with stellate cytoplasmic contours
Occasional foci with storiform pattern similar to nodular fasciitis
Some cases with keloid-like collagen
Small but conspicuous vessels
Open, gaping, thin-walled vessels with perivascular sclerosis often feature of mesenteric fibromatosis
 Gross photograph shows a large deep fibromatosis involving the shoulder. This lesion has eroded into the scapula, although typically fibromatoses do not erode bone. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Superficial fibromatoses
Palmar fibromatosis: Dupuytren contracture, Dupuytren disease
Plantar fibromatosis: Ledderhose disease
Penile fibromatosis: Peyronie disease
Knuckle pads
Deep fibromatosis: Aggressive fibromatosis, desmoid tumor
Definitions
Palmar fibromatosis
Nodular myofibroblastic proliferation of volar surface of hand that is prone to local persistence but does not metastasize
Plantar fibromatosis
Nodular myofibroblastic proliferation of plantar surface of foot that is prone to local persistence but does not metastasize
Peyronie disease
Penile fibrous lesion causing various deformities; initially pain with erection, erectile dysfunction
Knuckle pads
Well-circumscribed thickening of skin over metacarpophalangeal and, more commonly, proximal interphalangeal joints
Some associated with Dupuytren contractures, most idiopathic
Deep fibromatosis
Myofibroblastic proliferations of deep soft tissues with infiltrative growth pattern
Prone to local recurrences but do not metastasize
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Palmar fibromatosis
4-6% of Caucasian adults over 50 years of age
Reports of up to 75% of Celtic men
Uncommon in nonwhites
Marked male predominance
Plantar fibromatosis
1-2 per 100,000 persons per year (northern Europe)
Most patients 30-50 years of age
Slight male predominance
Penile fibromatosis
About 3.5% of white men over 50 years of age
Deep fibromatosis
2.4-4.43 new cases per 100,000 persons per year (Scandinavian data)
Presentation
Superficial fibromatoses present as nodular lesions on palms, soles, knuckles, or penis
Most common in older white men
Deep fibromatoses present as firm large masses
Relationship to age and gender
In children, no gender predominance: Lesions of shoulders, chest wall, back, thigh, head, and neck
In women in childbearing years: Abdominal wall
In older adults, no gender predominance: Lesions of shoulders, chest wall, back, thigh, head, and neck
Mesenteric fibromatoses
Most have asymptomatic abdominal mass
Gastrointestinal hemorrhage or perforation
Lesions associated with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP)
Risk of fibromatoses is 2.56/1,000 person-years
Comparative risk is 852x that of general population
Occasionally associated with scar (“cicatricial fibromatosis”)
Treatment
Superficial fibromatoses treated by excision
Nonsurgical treatments for penile lesions
Verapamil treatment administered by intraplaque injection
Colchicine, aminobenzoate potassium (Potaba), L-carnitine, and liposomal superoxide dismutase
Deep fibromatoses treated by wide excision
For unresectable lesions, radiation, chemotherapy, hormone therapy
Prognosis
Recurrences common for both superficial and deep fibromatoses
Occasional deaths from deep fibromatoses
FAP-associated mesenteric fibromatosis
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Superficial fibromatoses
Small (1-3 cm), nodular, firm, white lesions; some with gritty cut surface
Large, infiltrative, firm, white lesions; some with gritty cut surface
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Sweeping fascicles of myofibroblasts
Smooth nuclear membranes
Delicate nucleoli in most cells
Occasional cells with stellate cytoplasmic contours
Occasional foci with storiform pattern similar to nodular fasciitis
Uniformly distributed collagen
Some cases with keloid-like collagen
Prominent vascular pattern
Small but conspicuous vessels
Open, gaping, thin-walled vessels with perivascular sclerosis
Minimal background inflammation
Scattered lesional giant cells found in some plantar fibromatoses
Rarely found in palmar and deep fibromatoses
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree